Use Case: Uniswap V2 Stop Order Demo
Overview
This article focuses on the Uniswap V2 Stop Order Demo where a reactive contract listens for Sync events in a Uniswap V2 pool and triggers asset sales when the exchange rate hits a specified threshold. This demo extends the principles introduced in the Reactive Network Demo, which provides an introduction to building Reactive Contracts that respond to real-time events.
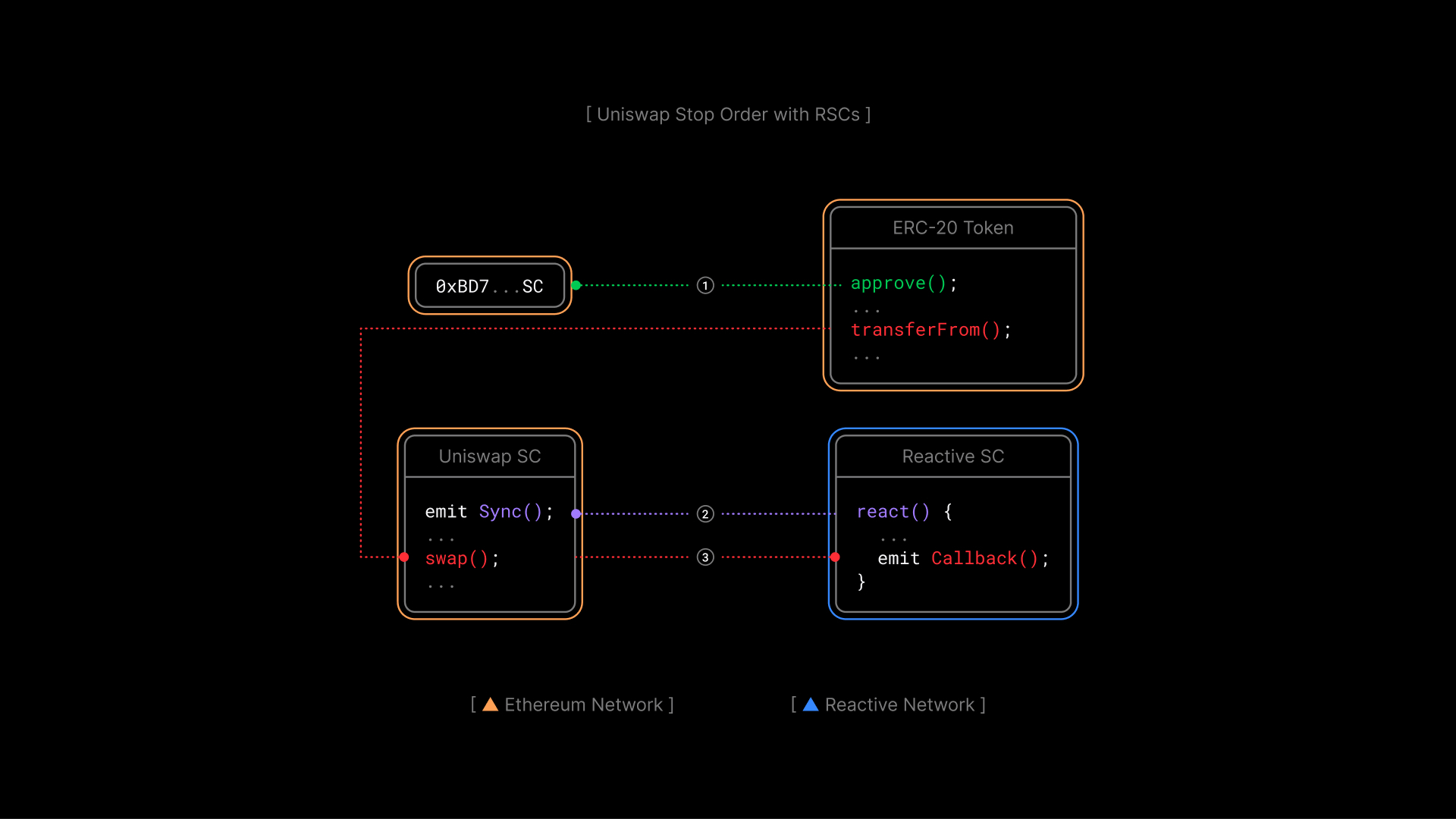
Contracts
-
Origin Chain Contract: UniswapDemoToken is a basic ERC-20 token with 100 tokens minted to the deployer's address. It provides integration points for Uniswap swaps.
-
Reactive Contract: UniswapDemoStopOrderReactive subscribes to a Uniswap V2 pair and stop order events. It checks if reserves fall below a threshold and triggers a stop order via callback.
function react(
uint256 chain_id,
address _contract,
uint256 topic_0,
uint256 topic_1,
uint256 topic_2,
uint256 /* topic_3 */,
bytes calldata data,
uint256 /* block_number */,
uint256 /* op_code */
) external vmOnly {
assert(!done);
if (_contract == stop_order) {
if (
triggered &&
topic_0 == STOP_ORDER_STOP_TOPIC_0 &&
topic_1 == uint256(uint160(pair)) &&
topic_2 == uint256(uint160(client))
) {
done = true;
emit Done();
}
} else {
Reserves memory sync = abi.decode(data, ( Reserves ));
if (below_threshold(sync) && !triggered) {
emit CallbackSent();
bytes memory payload = abi.encodeWithSignature(
"stop(address,address,address,bool,uint256,uint256)",
address(0),
pair,
client,
token0,
coefficient,
threshold
);
triggered = true;
emit Callback(chain_id, stop_order, CALLBACK_GAS_LIMIT, payload);
}
}
}
- Destination Chain Contract: UniswapDemoStopOrderCallback processes stop orders. When the Reactive Network triggers the callback, the contract verifies the caller, checks the exchange rate and token balance, and performs the token swap through the Uniswap V2 router, transferring the swapped tokens back to the client. After execution, the contract emits a
Stopevent, signaling the reactive contract to conclude. The stateless callback contract can be used across multiple reactive stop orders with the same router.
Further Considerations
The demo showcases essential stop order functionality but can be improved with:
- Dynamic Event Subscriptions: Supporting multiple orders and flexible event handling.
- Sanity Checks and Retry Policies: Adding error handling and retry mechanisms.
- Support for Arbitrary Routers and DEXes: Extending functionality to work with various routers and decentralized exchanges.
- Improved Data Flow: Refining interactions between reactive and destination chain contracts for better reliability.
Deployment
To deploy the contracts to Ethereum Sepolia and Reactive Lasna, clone the project and follow the Deployment & Testing steps. Replace the relevant keys, addresses, and endpoints as needed. Make sure all environment variables are correctly configured before proceeding.
Conclusion
In this article, we explored how reactive contracts operate in automating stop orders on Uniswap V2. We examined how they interact with Sync events, automate transactions, and use callback contracts for order completion. This provides practical insight into building responsive, decentralized financial tools.